一、基本信息
(1) 王鹏飞教授

王鹏飞 博士,特聘教授,博士生导师。国家级领军人才、国家级青年人才、美国光学学会会士(Optica Fellow)、爱尔兰都柏林科技大学荣誉教授、爱思唯尔(Elsevier)2019年中国高被引学者、Euroscience和欧盟玛丽居里学会终身会员。Elsevier期刊Infrared Physics & Technology 副编辑 Associate Editor、Journal of Lightwave Technology 副编辑 Associate Editor、Applied Optics 专栏编委 Topical Editor、Scientific Reports、Springer期刊Optical and Quantum Electronics 编委 Editor,《中国激光》、《红外与激光工程》青年编委。主要从事中红外波段光纤激光器、特种光学玻璃材料和集成光学器件等领域研究。主持国家自然科学基金委重点项目、重大项目课题、科技部政府间合作重点研发计划、国家留学基金委创新项目和黑龙江省自然科学基金重点项目等多个国家和省部级重点科研项目。在Nature Communications、ACS Sensors等国际学术期刊上发表学术论文200余篇,文章累计被引用6000余次,英文专著章节3篇,主编Nature Springer英文专著1本。中国硅酸盐学会特种玻璃分会理事、中国光学学会纤维光学与光子集成专业委员会委员、全国光学和光子学标准化技术委员会委员。
(2) 王顺宾副教授

王顺宾,1988年8月生于山东省潍坊市,博士,副教授,硕士生导师。2014-2017年就读于吉林大学微电子学与固体电子学专业,取得理学博士学位。主讲大学物理、光信息材料等课程,主要研究方向为稀土掺杂发光材料、特种玻璃及光纤制备、中红外光纤激光器、光纤光栅、微型谐振腔激光器等。2017年进入哈尔滨工程大学任教。现为物理与光电工程学院光子科学与技术研究中心教师。目前主持国家自然科学基金2项,黑龙江省自然科学基金1项,中央高校基础科研项目3项,参与国家自然科学基金重点项目1项。
(3) 贾世杰副教授

贾世杰,1989年生,博士,副教授,硕士生导师。2018年于吉林大学物理电子学专业取得工学博士学位。主讲光纤理论与技术、大学物理和激光技术与光纤激光器等课程,主要研究方向为光子玻璃器件、特种光纤与中红外光纤激光器等。《发光学报》青年编委。2018年进入哈尔滨工程大学任教。现为物理与光电工程学院光子科学与技术研究中心教师。目前主持国家自然科学基金1项,黑龙江省自然科学基金1项,中央高校基础科研项目3项,作为负责人参与科技部重点研发计划和国家自然科学基金重大项目各1项。
(4) 田可副教授

田可,1991年生,博士,副教授,硕士生导师。2019年于哈尔滨工程大学取得工学博士学位,先后在爱尔兰都柏林科技大学、日本冲绳科学技术大学院大学开展科研工作。美国光学学会(Optica)会员,日本冲绳科学技术大学院大学客座研究员,长期担任Photonics Res., Opt. Lett., Opt. Express, J. Lightwave Technol.等期刊审稿人。主讲大学物理实验等课程,主要研究方向为光纤传感、飞秒激光微加工、光学微腔等,已在Opt. Lett.、Opt. Express等国际期刊和会议上发表学术论文30余篇。
(5) 李真睿讲师

李真睿,1989年4月生黑龙江省哈尔滨市,博士,讲师,硕士生导师。圣彼得堡国立信息技术机械与光学大学联合培养硕士。2016年就读于吉林大学微电子学与固体电子学专业,取得理学博士学位。主讲非线性光纤光学等课程,主要研究方向为光纤激光器、非线性光纤光学等。2020年进入哈尔滨工程大学任教。现为物理与光电工程学院光子科学与技术研究中心教师。主持国家自然科学基金青年科学基金项目1项,参与国家自然科学基金重大项目1项,国家自然科学基金国家重大科研仪器研制项目1项。
(6) 李施讲师

李施,1992年2月生于吉林省洮南市,博士,讲师,硕士生导师。2017年就读于哈尔滨工程大学光学工程专业,取得工学博士学位。主讲大学物理,激光原理等课程,主要研究方向为脉冲光纤激光器、二维材料、非线性光学、光纤传感器等。《Frontiers in Sensors》编委。2020年进入哈尔滨工程大学任教。现为物理与光电工程学院光子科学与技术研究中心教师。
(7) 尹钰讲师

尹钰,1994年10月生于内蒙古自治区根河市,博士,讲师,硕士生导师。2017年就读于哈尔滨工程大学光学工程专业,取得工学博士学位。主讲大学物理、大学物理实验等课程,主要研究方向为光纤传感器、微纳光纤结构器件等。2021年进入哈尔滨工程大学任教,现为物理与光电工程学院光子科学与技术研究中心教师。主持国家自然科学基金青年科学基金项目1项。
二、 研究方向
1. 中红外波段光纤激光器

中红外波段激光光源在基础科学研究、光通信、生物医疗、环境污染监测以及国防安全等领域都有着非常重要的应用。与其他激光器相比,光纤激光器具有转换效率高、光束质量好、结构紧凑、可靠性好、稳定性高、寿命长、质量轻以及便于携带与集成等特性,使得其成为近年来研究中红外波段激光器的主要方向之一。
在中红外波段光纤激光器的研究领域,本研究团队主要研究兴趣是系统地发展中红外波段光纤激光器的理论、方法和技术,发展多种稀土掺杂的新型氟化物光纤及激光器。进行了如下工作:
制备多组分低损耗氟化锆、氟化铝、氟化锌、氟化铟基玻璃光纤。
利用Ho/Pr掺杂光纤在2.9 μm波段实现了2.2 W激光输出。
首次在中红外波段实现氟化铝光纤光栅刻写。
2. 特种光学玻璃材料


目前研究较多的激光增益玻璃基质材料主要有氟化物玻璃、多组分氧化物玻璃、硫系玻璃及石英玻璃等。总的来说,与氧化物玻璃相比,氟化物玻璃的声子能量低,透过窗口可以从紫外波段覆盖到中红外波段,透过率最高可达90%,同时具有较低的色散、较强的离子键性能和较高的稀土离子溶解度等优点。稀土离子在氟化物玻璃中的发光范围可以从紫外一直延伸到中红外波段,因此成为发光材料与红外光学器件等领域的研究热点。
在特种光学玻璃材料的研究领域,本研究团队主要研究方向是探索成玻稳定、物化性质良好的玻璃组分及优异的玻璃制备工艺,制备通过率高、中红外波段发光强度高的激光玻璃。进行了如下工作:
制备性质优异的TBY碲酸盐玻璃,PBG重金属氧化物玻璃,氟化锆、氟化铝、氟化锌、氟化铟基等氟化物玻璃。
研究了在Ho3+、Er3+、Dy3+等稀土离子掺杂玻璃中2.7 μm、2.9 μm、3.5 μm、3.9 μm等波段的发光性质。
以玻璃材料为基础,制备光学微球、微泡和光纤,为实现高性能中红外激光器件奠定基础。
3. 光纤传感技术及应用

光纤传感,包含对外界信号的感知和传输两种功能,这都需要依靠光纤本身来完成。光纤由于其工作频带宽,动态范围大,适合于遥测遥控,是一种优良的低损耗传输介质。同时在一定条件下,光纤特别容易接受被测量环境的加载,是一种优良的敏感元件,因而可以制备成为光纤传感器。光纤传感器与其它类型的传感器相比,最明显的优势包括:测量灵敏度高、可弯曲不易损坏、抗电磁干扰、防燃防爆、扛腐蚀性、可在高温高压下工作、结构简单小巧、可以承担低损耗远距离的信号传输工作等。
在光纤传感的研究领域,本研究团队主要研究方向是多模干涉传感器件、飞秒激光直写技术、回音壁微腔、微纳光子器件(包括微纳光纤耦合器、微光纤卷形谐振器、微光纤环形谐振器),研制多种高灵敏度的物理/化学/生物光纤传感器件。进行了如下工作:
系统研究了圆形、D形、平板形、角度抛磨形、葫芦形、气球形等多种几何形状在内的多模光纤的多模干涉原理、偏振依赖特性、矢量传感特性。
基于飞秒激光写入技术,成功在石英单模光纤的纤芯内平行写入马赫增尔干涉仪和光纤布拉格光栅、矢量弯曲光纤耦合器。
外径为125微米的石英光纤可以在经过拉锥后将尺寸降低至几个微米或是纳米量级,并被灵活地制备成为微纳光纤耦合器,或是经过打结和缠绕等方式构成谐振器,用作高灵敏的湿度、温度、痕量重金属离子的检测。
三、 科研成果
1. Two-watt mid-infrared laser emission in robust fluorozirconate fibers
Changjun Xu, Jiquan Zhang, Xiaotong Zhao, Haiyan Zhao, Fengzi Ling, Shijie Jia, Gerald Farrell, Shunbin Wang, and Pengfei Wang, Optics Letters, 2022

To the best of our knowledge, we report here the first demonstration of 2.9 µm laser emission from in-house fabricated Ho3+/Pr3+ co-doped ZBYA glass fiber. The fiber was fabricated based on the ZBYA glass with compositions of ZrF4-BaF2-YF3-AlF3-PbF2-HoF3-PrF3. Under the pump of a 1150 nm Raman fiber laser, the maximum unsaturated output power of 2.16 W was obtained in a 15 cm long gain fiber with a slope efficiency of 24%. The influence of rare-earth doping concentration on laser performance was also investigated. The result indicates that ZBYA glass fibers have potential for using as a fluorozirconate glass gain fiber for mid-infrared fiber lasers.
2. Direct femtosecond laser inscription of Bragg gratings in Ho3+/Pr3+ co-doped AlF3-based glass fibers for a 2.86 μm laser
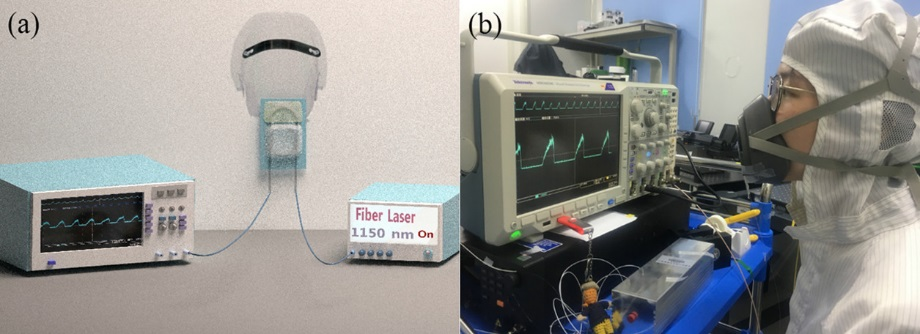
Niannian Xu, Zhiyong Yang, Jiquan Zhang, Nian Lv, Mo Liu, Ruoning Wang, Zhenrui Li, Shijie Jia, Gilberto Brambilla, Shunbin Wang, and Pengfei Wang, Optics Letters, 2022
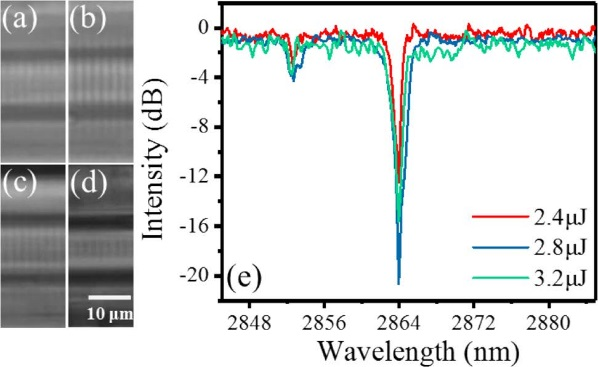
In this Letter, we report the fabrication of fiber Bragg gratings (FBGs) in home-made Ho3+/Pr3+ co-doped singlecladding fluoroaluminate (AlF3) glass fibers and its application in watt-level lasing at the mid-infrared (MIR) wavelength of 2.86 μm. The FBGs were inscribed using an 800 nm femtosecond (fs) laser direct-writing technique. The FBG properties were investigated for different pulse energies, inscription speeds, grating orders, and transversal lengths. A second-order FBG with a high reflectivity of 99% was obtained at one end of a 16.5-cm-long gain fiber. Under 1150 nm laser pumping, this fiber yielded a power exceeding 1 W at 2863.9 nm with an overall laser efficiency of 17.7%. The fiber laser showed a FWHM bandwidth of 0.46 nm and long-term spectral stability.
3. Enhanced 3.9 μm emission from diode pumped Ho3+/Eu3+ codoped fluoroindate glasses
Zhi Zhang, Ruicong Wang, Mo Liu, Shunbin Wang, Jie Zhang, Gilberto Brambilla, Shijie Jia, and Pengfei Wang, Optics Letters, 2021
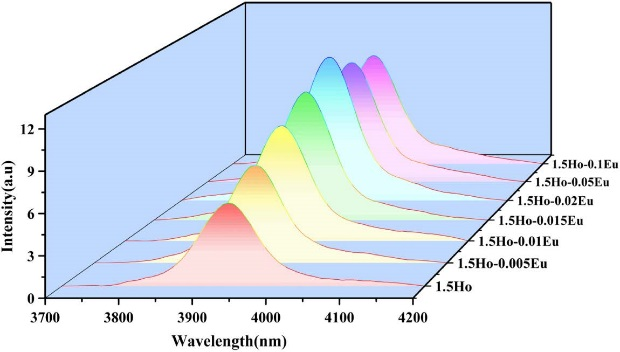
The use of Eu3+ codoping for enhancing the Ho3+:5I5→5I6 emission in fluoroindate glasses shows that Eu3+ could depopulate the lower laser state Ho3+:5I6 while having little effect on the upper state Ho3+:5I5, resulting in greater population inversion. The Ho3+/Eu3+ codoped glass has high spontaneous transition probability (6.31s-1) together with large emission cross section (7.68×10-21cm2). This study indicates that codoping of Ho3+ with Eu3+ is a feasible alternative to quench the lower energy level of the 3.9 µm emission and the Ho3+/Eu3+ codoped fluoroindate glass is a promising material for efficient 3.9 µm fiber lasers.
4. High-Performance Ultrafast Humidity Sensor Based on Microknot Resonator-Assisted Mach-Zehnder for Monitoring Human Breath
Yating Yi, Yuxuan Jiang, Haiyan Zhao, Gilberto Brambilla, Yaxian Fan, and Pengfei Wang, ACS Sensors, 2020
Monitoring the dynamic humidity requires sensors with fast response and anti-electromagnetic interference, especially for human respiration. Here, an ultrafast fiber-optic breath sensor based on the humidity-sensitive characteristics of gelatin film is proposed and experimentally demonstrated. The sensor consists of a microknot resonator superimposed on a Mach-Zehnder (MZ) interferometer produced by a tapered single-mode fiber, which has an ultrafast response (84 ms) and recovery time (29 ms) and a large dynamic transmission range. The humidity in dynamic ambient causes changes in the refractive index of gelatin coating, which could trigger spectral intensity transients that can be explicitly distinguished between the two states. The sensing principle is analyzed using the traditional transfer-matrix analysis method. The influence of coating thickness on the sensor’s trigger threshold is further investigated. Experiments on monitoring breath patterns indicate that the proposed breath sensor has high repeatability, reliability, and validity, which enable many other potential applications such as food processing, health monitoring, and other biomedical applications.
5. Ultra-compact in-core-parallel-written FBG and Mach-Zehnder interferometer for simultaneous measurement of strain and temperature
Ke Tian, Mingyuan Zhang, Zhiyuan Zhao, Ruoning Wang, Dejun Liu, Elfed Lewis, Gerald Farrell, and Pengfei Wang, Optics Letters, 2021
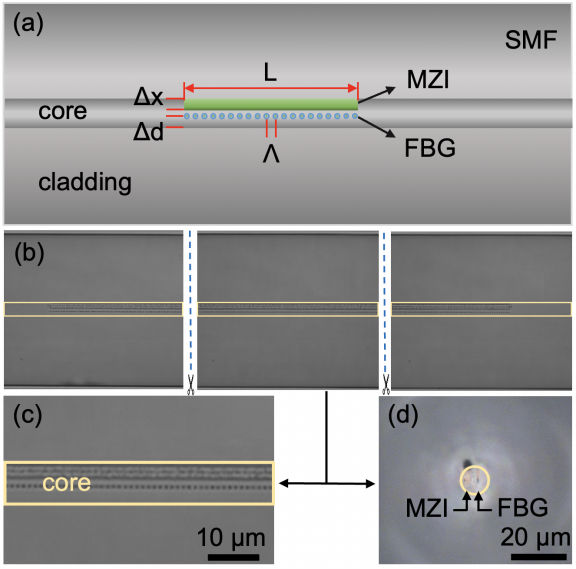
An ultra-compact in-core-parallel-written fiber Bragg grating (FBG) and Mach-Zehnder interferometer (MZI) for simultaneous measurement of strain and temperature is described. The FBG and MZI are written spatially parallel in the same section of fiber core using a femtosecond laser, forming an ultra-compact device, which is different from the previously developed axial cascade of different structures. Due to the weak coupling between the FBG and the MZI, their individual extinction ratios are traded off by optimizing their writing position and separation, and extinction ratios of 5.9 dB for the FBG and 10 dB for the MZI are achieved. Experimental results show that the FBG and MZI have different sensitivities for strain and temperature, allowing this device to measure strain and temperature simultaneously. In addition, since both the FBG and MZI are written in the fiber core, this ultra-compact device is proven to be impervious to ambient humidity, making it a promising candidate for accurate industrial strain and temperature measurements.
6. Investigation on the Dependence of Directional Torsion Measurement on Multimode Fiber Geometry
Ruoning Wang, Ke Tian, Meng Zhang, Mingyuan Zhang, Gerald Farrell, Elfed Lewis, Libo Yuan, and Pengfei Wang, Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2022

The torsion measurement and torsion direction discrimination characteristics of a multimode fiber (MMF) geometry in a singlemode-multimode-singlemode (SMS) fiber structure are investigated theoretically and experimentally. Three different geometries of MMFs, including circular symmetric MMF, axisymmetric MMF, and asymmetric MMF were fabricated based on a fiber polishing technique. The torsion response characteristics of a MMF depends on the birefringence within the MMF, as birefringence is related to the twist rate of the fiber. The experimental results demonstrate that the unpolished MMF with a circular asymmetric refractive index (RI) distribution has no wavelength response to torsion, and the single-side polished MMF with an axisymmetric RI distribution can measure torsion, but it does not have the ability to discriminate torsion direction. It is found that an MMF section with two polished surfaces at an angle to each other results in a departure from the symmetrical RI distribution, which introduces elliptical birefringence into the MMF. As a result, directional torsion measurement is achieved with sensitivities of 0.162 nm/(rad/m) clockwise and -0.139 nm/(rad/m) counterclockwise. The MMF geometry presented provides a new approach to torsion direction discrimination and shows good application potential in practical torsion vector measurement.
7. Ultra-high-resolution detection of Pb2+ ions using a black phosphorus functionalized microfiber coil resonator
Yu Yin, Shi Li, Shunbin Wang, Shijie Jia, Jing Ren, Gerald Farrell, Elfed Lewis and Pengfei Wang, Photonics Research, 2019

A black phosphorus (BP) functionalized optical fiber sensor based on a microfiber coil resonator (MCR) for Pb2+ ion detection in an aquatic environment is presented and experimentally demonstrated. The MCR-BP sensor is manufactured by winding a tapered microfiber on a hollow rod composed of a low-refractive-index polycarbonate (PC) resin with the BP deposited on the internal wall of the rod. Based on the propagation properties of the MCR, the chemical interaction between the Pb2+ ions and the BP alters the refractive index of the ambient environment and thus results in a detectable shift in the transmission spectrum. The resonance wavelength moves towards longer wavelengths with an increasing concentration of Pb2+ ions, and the sensor has an ultra-high detection resolution of 0.0285 ppb (parts per billion). The temperature dependence is 106.95 pm/°C due to the strong thermo-optic and thermal-expansion effect of the low-refractive-index PC resin. In addition, the sensor shows good stability over a period of 15 days. The local pH also influences the sensor, with the resonance wavelength shift increasing as pH approaches a value of 7 but then decreasing as the pH value increases further due to the effect of the BP layer by H+ and OH− ions. The sensor shows the potential for high-resolution detection of Pb2+ ions in a liquid environment with the particular advantages of having a simple structure, ease of fabrication, low cost, low loss, and simple interrogation.
四、 近三年发表论文列表
[1] Changjun Xu, Jiquan Zhang, Xiaotong Zhao, Haiyan Zhao, Fengzi Ling, Shijie Jia, Gerald Farrell, Shunbin Wang, and Pengfei Wang*, " Two-watt mid-infrared laser emission in robust fluorozirconate fibers," Optics Letters, vol. 47, no. 6, pp. 1399-1402, 2022. (*Corresponding author)
[2] Niannian Xu, Zhiyong Yang, Jiquan Zhang, Nian Lv, Mo Liu, Ruoning Wang, Zhenrui Li, Shijie Jia, Gilberto Brambilla, Shunbin Wang, and Pengfei Wang*, " Direct femtosecond laser inscription of Bragg gratings in Ho3+/Pr3+ co-doped AlF3-based glass fibers for a 2.86 μm laser," Optics Letters, vol. 47, no. 3, pp. 597-600, 2022. (*Corresponding author)
[3] Yating Yi, Yuxuan Jiang, Haiyan Zhao, Gilberto Brambilla, Yaxian Fan, and Pengfei Wang*, "High-Sensitivity Humidity Sensor Based on Microknot Resonator Assisted Agarose-Coated Mach-Zehnder Interferometer," Journal of Lightwave Technology, accepted for publication. (*Corresponding author)
[4] Jie Zhang, Ruicong Wang, Mo Liu, Shunbin Wang, Zhi Zhang, Gerald Farrell, Shijie Jia, and Pengfei Wang*, "ZnF2 modified AlF3-based fluoride glasses with enhanced mid-infrared 3.5 μm emission," Journal of the American Ceramic Society, revised. (*Corresponding author)
[5] Pengfei Wang, Shi Li, Fengzi Ling, Gerald Farrell, Elfed Lewis, and Yu Yin*. "All-optical modulator based on an microfibre coil resonator functionalized with MXene," Optical Fiber Technology, accepted for publication. (*Corresponding author)
[6] Ke Tian, Mingyuan Zhang, Zhiyuan Zhao, Ruoning Wang, Dejun Liu, Xin Wang, Elfed Lewis, Gerald Farrell, and Pengfei Wang*, "Ultra-compact in-core-parallel-written FBG and Mach-Zehnder interferometer for simultaneous measurement of strain and temperature," Optics Letters, vol. 46, no. 22, pp. 5595-5598, 2021. (*Corresponding author)
[7] Jin Yu, Yanqiu Du, Xiaotong Zhao, Shijie Jia, Zhenrui Li, Shunbin Wang, and Pengfei Wang*, "2 µm lasing from Tm3+-doped PbO-PbF2-Bi2O3-Ga2O3 glass microspheres," Optics Letters. vol. 46, no. 20, pp. 5084-5087, 2021. (*Corresponding author)
[8] Meng Zhang, Ruoning Wang, Ke Tian, Jibo Yu, Gilberto Brambilla, Libo Yuan and Pengfei Wang*, "Optical detection of ammonia in water using integrated up-conversion fluorescence in a fiberized microsphere," Journal of Lightwave Technology, vol. 39, no. 22, pp. 7303-7306, 2021. (*Corresponding author)
[9] Xingchen Lin, Pengfei Wang, Hongbo Zhu*, Yawei Zhang, Yongqiang Ning. "A novel method for the welding of tailor-welded blanks with different thicknesses based on the diode laser source," Optics and Laser Technology, vol. 141, pp. 107100, 2021.
[10] Xingchen Lin, Pengfei Wang, Hongbo Zhu*, Ziqi Song, Yawei Zhang, Yongqiang Ning. "A novel processing method based on the 3-spot diode laser source for the laser cladding of stainless-steel ball valves," Optics and Laser Technology, vol. 141, pp. 107142, 2021.
[11] Lin She, Qianyu Qi, Peiqing Zhang, Shixun Dai, Yuxuan Jiang, Weimin Sun, Shijie Jia, Shunbin Wang, Gilberto Brambilla, and Pengfei Wang*, " Mid-infrared ?uoroindate glass long-period fber grating by femtosecond laser inscription," Infrared Physics and Technology, vol. 116, pp. 103808, 2021. (*Corresponding author)
[12] Pengfei Wang, Jie Zhang, Jiquan Zhang, Shijie Jia, Lijun Wang, Yongqiang Ning, Hangyu Peng, Gerald Farrell, Shunbin Wang* and Ruicong Wang*, "3.5 μm emission in Er3+ doped fluoroindate glasses under 635 nm laser excitation," Journal of Luminescence, vol. 237, pp. 118200, 2021.
[13] Jiquan Zhang, Haiyan Zhao, Ruicong Wang, Angzhen Li, Jie Zhang, Shijie Jia, Gilberto Brambilla, Shunbin Wang*, and Pengfei Wang*, "3.9 μm emission in Nd3+ sensitized Ho3+ doped fluoroaluminate glasses," Journal of Alloys and Compounds, pp. 161684, 2021. (*Corresponding author)
[14] Jiquan Zhang, Mo Liu, Jin Yu, Ruicong Wang, Shijie Jia, Zijun Liu, Gerald Farrell,Shunbin Wang* and Pengfei Wang*, "Praseodymium mid-infrared emission in AlF3-based glass sensitized by ytterbium," Optics Express, vol. 29, no. 21, pp. 34166-34174,2021. (*Corresponding author)
[15] Jiquan Zhang, Ruicong Wang, Xin Wang, Wenhao Li, Mo Liu, Shijie Jia, Lijun Wang, Yongqiang Ning, Hangyu Peng, Gilberto Brambilla, Shunbin Wang* and Pengfei Wang*, "Efficient 3.5 μm mid-infrared emission in heavily Er3+-doped fluoroaluminate glasses and its emission mechanism." Journal of Luminescence, vol. 238, pp. 118301, 2021. (*Corresponding author)
[16] Mo Liu, Jiquan Zhang, Jie Zhang, Zhi Zhang, Gerald Farrell, Gilberto Brambilla, Shunbin Wang and Pengfei Wang*, “2.4 μm fluorescence of holmium doped fluoroaluminate glasses”, Journal of Luminescence, vol. 238, pp. 118265, 2021. (*Corresponding author)
[17] Angzhen Li, Ke Tian, Jibo Yu, Rashmi A. Minz, Jonathan M. Ward, Samir Mondal, Pengfei Wang* and Síle Nic Chormaic*, "A packaged whispering gallery resonator device based on an optical nanoantenna coupler," Optics Express, vol. 29, no. 11, pp. 16879-16886, 2021. (*Corresponding author)
[18] Mo Liu, Jiquan Zhang, Niannian Xu, Xinwei Tian, Shunbin Wang*, Gilberto Brambilla, and Pengfei Wang*, "Room-temperature Watt-level and Tunable ~3 μm ultra-stable Lasers in Ho3+/Pr3+ Co-doped AlF3-based Glass Fiber," Optics Letters, vol. 46, no. 10, pp. 2417-2420, 2021. (*Corresponding author)
[19] Zhi Zhang, Ruicong Wang, Mo Liu, Shunbin Wang, Jie Zhang, Gilberto Brambilla, Shijie Jia, and Pengfei Wang*, "Enhanced 3.9 μm emission from diode pumped Ho3+/Eu3+ co-doped fluoroindate glasses," Optics Letters, vol. 46, no. 9, pp. 2031-2034, 2021. (*Corresponding author)
[20] Yuxuan Jiang, Yating Yi, Gilberto Brambilla, and Pengfei Wang*, " High-sensitivity, fast-response ethanol gas optical sensor based on a dual microfiber coupler structure with the Vernier effect," Optics Letters, vol. 46, no. 7, pp. 1558-1561, 2021. (*Corresponding author)
[21] Yating Yi, Yuxuan Jiang, Haiyan Zhao, Gilberto Brambilla, Yaxian Fan and Pengfei Wang*, "A High-Performance Ultrafast Humidity Sensor Based on Micro-Knot Resonator-Assisted Mach-Zehnder for Monitoring Human Breath," ACS Sensors, vol. 5, no.11, pp. 3404-3410, 2020. (*Corresponding author)
[22] Jibo Yu, Jiquan Zhang, Ruicong Wang, Angzhen. Li, Meng Zhang, Shunbin Wang, Pengfei Wang*, Jonathan Ward and Sile Nic Chormaic*, "A tellurite glass optical microbubble resonator," Optics Express, vol. 28, no. 22, pp. 32858-32868, 2020. (*Corresponding author)
[23] Yu Yin, Shi Li, Jing Ren, Yanqiu Du, Gerald Farrell, Gilberto Brambilla, Pengfei Wang*, "All-optical modulation in Black Phosphorus functionalized microfibre coil resonator," Measurement Science and Technology, vol. 32(1): 015202, 2020. (*Corresponding author)
[24] Pengfei Wang, Han Zhang, Yu Yin, Qiuyun Ouyang, Yujin Chen, Elfed Lewis, Gerald Farrell, Masaki Tokurakawa, Sulaiman Wadi Harun, Cong Wang and Shi Li*, "NiS2 as a broadband saturable absorber for ultrafast pulse lasers," Optics & Laser Technology, vol. 132, pp. 106492, 2020. (*Corresponding author)
[25] Jin Yu, Meng Zhang, Yanqiu Du, Gilberto Brambilla, Shijie Jia, Yongqiang Ning, Hangyu Peng, Shunbin Wang,* and Pengfei Wang*, "Broadband 2.7 μm mid-infrared emissions in Er3+-doped PbO-PbF2-Bi2O3-Ga2O3 glasses," Optics Letters, vol. 45, no. 16, pp. 4638-4641, 2020. (*Corresponding author)
[26] Xin Wang, Pengfei Wang*, Ke Tian, Shijie Jia, Shunbin Wang, and Gilberto Brambilla, "Ultra-broadband near-infrared photoluminescence in Er3+-Ni2+co-doped transparent glass ceramics containing nano-perovskite KZnF3," Ceramics International, vol. 46, pp. 25987-25991. (*Corresponding author)
[27] Haiyan Zhao, Ruicong Wang, Xin Wang, Shijie Jia, Yaxian Fan, Elfed Lewis, Gerald Farrell, Shunbin Wang, and Pengfei Wang*, "Intense mid-infrared emission at 3.9 μm in Ho3+-doped ZBYA glasses for potential use as a fiber laser," Optics Letters, vol. 45, no. 15, pp. 4272-4275, 2020. (*Corresponding author)
[28] Xin Wang, Wenhao Li, Haiyan Zhao, Shunbin Wang, Shijie Jia, Yongkang Dong,Yanqiu Du, Gilberto Brambilla, and Pengfei Wang*, "Yb3+-Yb3+ Cooperative Upconversion in Oxyfluoride Glass and Glass Ceramics," Journal of Luminescence, vol. 226, pp. 117461, 2020. (*Corresponding author)
[29] Pengfei Wang, Yating Yi, Xin Wang, Angzhen Li, Shijie Jia, Yaxian Fan, Gilberto Brambilla, Shunbin Wang*, Haiyan Zhao*, "Tm3+-doped fluorotellurite glass microsphere resonator laser at 2.3 μm," Optics Letters, vol. 45, no. 13, pp. 3553-3556, 2020. (*Corresponding author)
[30] Ke Tian, Ruoning Wang, Meng Zhang, Xianfan Wang, Xin Wang, Guoyong Jin, Elfed Lewis, Gerald Farrell, and Pengfei Wang*, "Simultaneous measurement of displacement and temperature based on two cascaded balloon-like bent fibre structures," Optical Fiber Technology, vol. 58, pp. 102277, 2020. (*Corresponding author)
[31] Ke Tian, Meng Zhang, Jibo Yu, Yuxuan Jiang, Haiyan Zhao, Xin Wang, Dejun Liu, Guoyong Jin, Elfed Lewis, Gerald Farrell and Pengfei Wang*, "High sensitivity, low temperature-crosstalk strain sensor based on a microsphere embedded Fabry-Perot interferometer," Sensors and Actuators A, vol. 310, pp. 112048, 2020. (*Corresponding author)
[32] Ruicong Wang, Jiquan Zhang, Haiyan Zhao, Xin Wang, Shijie Jia, Haitao Guo, Shixun Dai, Peiqing Zhang, Gilberto Brambilla, Shunbin Wang*, and Pengfei Wang*, "3.9 μm emission and energy transfer in ultra-low OH-, Ho3+ /Nd3+ co-doped fluoroindate glasses," Journal of Luminescence, vol. 225, pp. 117363, 2020. (*Corresponding author)
[33] Ruoning Wang, Ke Tian, Meng Zhang, Yuxuan Jiang, Libo Yuan, Guoyong Jin, Gerald Farrell, Elfed Lewis, and Pengfei Wang*, "Investigation on the Polarization Dependence of an Angled Polished Multimode Fibre Structure," Journal of Lightwave Technology, vol. 38, no. 16, pp. 4520-4525, 2020. (*Corresponding author)
[34] Meng Zhang, Ke Tian, Shunbin Wang, Libo Yuan, Gerald Farrell, Elfed Lewis, and Pengfei Wang*, "Color Variation of the Up-conversion Luminescence in Er3+-Yb3+ Co-doped Lead Germanate Glasses and Microsphere Integrated Devices," Journal of Lightwave Technology, vol. 38, no. 16, pp. 4397-4401, 2020. (*Corresponding author)
[35] Xiaosong Lu, Jianhui Li, Lu Yang, Jing Ren, Mingyang Sun, Anping Yang, Zhiyong Yang, Ravinder Kumar Jain, and Pengfei Wang*, "Ultrabroad 2.5-5.5 μm mid-Infrared emission from Co2+/Fe2+ codoped nano-chalcogenide glass composite," Optics Letters, vol. 45, no. 10, pp. 2676-2679, 2020. (*Corresponding author)
[36] Xin Wang., Jibo Yu, Haiyan Zhao, Xiaosong Lu, Wenhao Li, Ke Tian, Pengfei Wang*, "1.88 μm laser emission from Tm3+ doped fluorosilicate glass microspheres with excellent stability and high damage threshold." Journal of Luminescence, vol. 220, pp. 117028, 2020. (*Corresponding author)
[37] Haidong Liang, Yuxuan Jiang, Xianfan Wang, Elfed Lewis and Pengfei Wang*, "All-Fiber Optic Displacement Sensing System for an Ilizarov Transverse Tibial Bone Transport device," Applied Optics, vol. 59, no. 7, pp. 2077-2084, 2020. (*Corresponding author)
[38] Yuxuan Jiang, Yating yi, Gilberto Brambilla and Pengfei Wang*, "Ultra-high-sensitivity refractive index sensor based on dual-microfiber coupler structure with Vernier effect," Optics Letters, vol. 45, no. 5, pp. 1268-1271, 2020. (*Corresponding author)
[39] Shunbin Wang, Jiquan Zhang, Shijie Jia, Gilberto Brambilla, Niannian Xu and Pengfei Wang*, "2.9 µm lasing from Ho3+/Pr3+ co-doped AlF3 based glass fiber pumped by a 1150 nm laser, " Optics Letters, vol. 45, no. 5, pp. 1216-1219, 2020. (*Corresponding author)
[40] Ke Tian, Jibo Yu, Xin Wang, Haiyan Zhao, Dejun Liu, Elfed Lewis, Gerald Farrell, and Pengfei Wang*,"A miniature Fabry-Perot interferometer based on a movable microsphere reflector," Optics Letters. vol. 45, no. 3, pp. 787-790, 2020. (*Corresponding author)
[41] Jibo Yu, Xin Wang, Wenhao Li, Meng Zhang, Jiquan Zhang, Ke Tian, Yanqiu Du, Síle Nic Chormaic and Pengfei Wang*, "An experimental and theoretical investigation of a 2 μm wavelength low-threshold microsphere laser," Journal of Lightwave Technology, vol.38, no. 7, pp. 1880-1886, 2020. (*Corresponding author)
[42] Ruicong Wang, Haiyan Zhao, Meng zhang, Jiquan Zhang, Shijie Jia, Jun Zhang, Hangyu Peng, Gilberto Brambilla, Shunbin Wang, and Pengfei Wang*, "Enhancement mechanisms of Tm3+-codoping on 2 μm emission in Ho3+ doped fluoroindate glasses under 888 nm laser excitation," Ceramics International, vol. 46, no. 1, pp. 6973-6977, 2020. (*Corresponding author)
[43] Xiaosong Lu, Jianhui Li, Lu Yang, Runan Zhang, Yindong Zhang, Jing Ren*, Aurelian Catalin Galca, Mihail Secu, Gerald Farrell, and Pengfei Wang*, "Third-order optical nonlinearity properties of CdCl2-modifed Ge–Sb–S chalcogenide glasses," Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, vol. 528, pp. 119757, 2020. (*Corresponding author)
[44] Haiyan Zhao, Shijie Jia, Xin Wang, Ruicong Wang, Xiaosong Lu, Yaxian Fan, M asaki Tokurakawa, Gilberto Brambilla, Shunbin Wang, and Pengfei Wang*, "Investigation of Dy3+/Tm3+ co-doped ZrF4-BaF2-YF3-AlF3 fluoride glass for efficient 2.9 μm mid-infrared laser applications," Journal of Alloys and Compounds, vol. 817, pp. 152754, 2020. (*Corresponding author)
[45] Haiyan Zhao, Yating Yi, Xin Wang, Angzhen Li, Anping Yang, Zhiyong Yang, Yaxian Fan, Shijie Jia, Elfed Lewis, Gilberto Brambilla, Shunbin Wang, and Pengfei Wang*, "Triple-wavelength lasing at 1.50 μm, 1.84 μm and 2.08 μm in a Ho3+/Tm3+ co-doped fluorozirconate glass microsphere," Journal of Luminescence, vol. 219, pp. 116889, 2020. (*Corresponding author)
[46] Angzhen Li, Yongkang Dong, Shunbin Wang, Shijie Jia, Gilberto Brambilla, and Pengfei Wang*, "Infrared-laser and upconversion luminescence in Ho3+-Yb3+ codoped tellurite glass microsphere," Journal of Luminescence, vol. 218, pp. 116826, 2020. (*Corresponding author)
[47] Xiaosong Lu, Runan Zhang, Yingdong Zhang, Shaoqian Zhang, Jing Ren*, Lukas Strizik, Tomas Wagner, Gerald Farrell, and Pengfei Wang*, "Crystal-Field Engineering of Ultrabroadband Mid-Infrared Emission in Co2+-doped Nano-Chalcogenide Glass Composites," Journal of the European Ceramic Society, vol. 40, pp. 103-107, 2020. (*Corresponding author)
[48] Sameer Salam, A. H. H. Al-Masoodi, P. Wang, and S. W. Harun, "Hybrid organic small molecules as a saturable absorber for passive Q-switching in erbium-doped fiber laser," OSA Continuum, vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 177-185, 2020.
五. 招生意向
王鹏飞教授课题组成员:王鹏飞教授,王顺宾副教授,贾世杰副教授,田可副教授,李真睿讲师,李施讲师,尹钰讲师。
团队目前承担多项国家科技部重点专项、中组部、国家自然基金委及省部级重点项目,具有充足的经费支持。
欢迎具有光电、物理学和无机化学材料等相关专业背景的本科生和硕士研究生报考本课题组,在光纤激光器、特种激光玻璃材料和光纤传感技术等热点研究领域进行探索和钻研。研究生在读期间,表现优异者可推荐到英国、爱尔兰、意大利、日本或澳大利亚等国外知名高校和研究机构,开展博士/硕士联合培养研究(为期1年)。
硕士专业:光学工程(工学);物理学(理学)
博士专业:光学工程(一级学科点)
博士后流动站:光学工程(一级学科点)
博士后、访问学者申请人应有以下一项或者多项研究背景:光学、物理学、材料科学。
联系方式:王鹏飞教授:pengfei.wang@tudublin.ie
王顺宾副教授:shunbinwang@hrbeu.edu.cn
贾世杰副教授:jiasj@hrbeu.edu.cn
田可副教授:ketian@hrbeu.edu.cn
李真睿讲师:lizr20@hrbeu.edu.cn
李施讲师:LScount@hrbeu.edu.cn
尹钰讲师:cbyy@hrbeu.edu.cn
